The Content:
Using the Color scheme
While designing web pages, computer applications, or house interiors, we need to find good color scheme - set of colors producing the best impression. For every tint there are colors which it can coexist with, and which it can't. Some combinations are uncomfortable, or disturbing - while others are pleasant.
Experienced designers choose colors intuitively, many people can smell which colors go together well and which don't. However, finding the good combination of colors may be sometimes long and gruelling work. The color theory makes the work easier. This tool will find set of colors you can start with, and it may facilitate your looking for the optimal color palette.
This application generates color schemes of several types. Every scheme is based on one (base) color, which is supplemented with additional colors making together the best optical imperssion - using one of the authentic algorithms.
Selecting the base color
The base color can be set in several ways. The application works primarily with the color wheel, and with colors defined by it - hue (the angle determining position of the color on the wheel), saturation (100 % is the most saturated color, 0 is a shade of gray), and brightness (100 % is lightest shade, 0 is black). Warm colors (purple to yellow) and cold colors (yellow-green to violet) are marked here as well.
We can choose one of the elemetary colors on the wheel by clicking on its circle. Primary colors (red, yellow, blue) correspond to angles 0°, 120°, and 240°, secondary colors (orange, green, violet) to angles 60°, 180°, and 300°, tertiary colors are between them. Smaller circles (multiples of 15°) are standing for transitional colors. Clicking on any of these colors, you'll set it as the base color.
You can change parameters of the base color (hue, saturation, brightness) in the input fields. There is a scale 0-360° inside the color wheel, containing a small pointer corresponding to the angle of actual color. Clicking on this scale you can change the hue without changing brightness and/or saturation (you have to click, you cannot drag the pointer). The angle the cursor points at is shown in the browser's status line. Similarly, you can set saturation and/or brightness by clicking on the scales beside the color wheel.
Important note: This tool doesn't use the standard HSV or HSB model (the same HSV/HSB values ie. in Photoshop describe different colors!). The color wheel used here differs from the RGB spectre used on computer screens, it's more in accordance with the classical color theory. This is also why some colors (especially shades of blue) make less bright shades than the basic colors of the RGB-model. In plus, the RGB-model uses red-green-blue as primary colors, but the red-yellow-blue combination is used here. This deformation also causes incompatibility in color conversions from RGB-values. Therefore, the RGB input (eg. the HTML hex values like #F854A9) is not possible.
Color schemes
The resulting color set is made by installing the base color into one of the color schemes. You can select the scheme from the menu on the right. Several schemes allow additional settings, which are displayed bellow the menu. You can choose one of following schemes:
Monochromatic
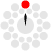 Monochormatic scheme is based on only one color tint, and uses only variations made by changing its saturation and brightness. Black and white colors are always added. The result is comfortable for eyes, even when using aggressive color. However, it's harder to find accents and highlights.
Monochormatic scheme is based on only one color tint, and uses only variations made by changing its saturation and brightness. Black and white colors are always added. The result is comfortable for eyes, even when using aggressive color. However, it's harder to find accents and highlights.
The application makes only several monochromatic variants of each color. You'll be able to make others - more or less saturated, lighter or darker. Monochromatic variations are made for each color in other schemes, too. They are displayed in the color palette bellow the color sample.
Contrast
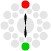 Base color is supplemented with its complement (color on the opposite side of the wheel). One warm and one cold color is always created - we have to consider, which one will be dominant, and if the result should look warm, or cold. Suitable monochromatic variations of this two colors may be added to the scheme.
Base color is supplemented with its complement (color on the opposite side of the wheel). One warm and one cold color is always created - we have to consider, which one will be dominant, and if the result should look warm, or cold. Suitable monochromatic variations of this two colors may be added to the scheme.
"Soft" contrast
 Base color is supplemented with two colors, placed identically on both sides of its complement. Unlike the "sharp" contrast, this scheme is often more comfortable for the eyes, it's softer, and has more space for balancing warm and cold colors.
Base color is supplemented with two colors, placed identically on both sides of its complement. Unlike the "sharp" contrast, this scheme is often more comfortable for the eyes, it's softer, and has more space for balancing warm and cold colors.
Additional input field (will be displayed bellow the scheme menu) sets the distance of these colors from the base color complement. The less the value is, the closer the colors are to the contrast color, and are more similar. The best value is between 15-30°. Higher values aren't too suitable - except the shift by 60°, which makes another color scheme, the triade:
Triade
The triade is made by three colors evenly distributed on the thirds of the color wheel (by 120 degrees). The triade-schemes are vibrating, full of energy, and have large space to make contrasts, accents and to balance warm and cold colors. You can make the triade in the "soft contrast" scheme setting the distance to 60°.
"Double-contrast"
 This scheme is made by a pair of colors and their complements. It's based on the tetrade - the foursome of colors evenly distributed on the fourths of the color wheel (by 90 degreees). The tetrade is very aggressive color scheme, requiring very good planning and very sensitive approach to relations of these colors.
This scheme is made by a pair of colors and their complements. It's based on the tetrade - the foursome of colors evenly distributed on the fourths of the color wheel (by 90 degreees). The tetrade is very aggressive color scheme, requiring very good planning and very sensitive approach to relations of these colors.
Less distance between two base colors causes less tension in the result. However, this scheme is always more "nervous" and "action" than other schemes. While working with it, we have to take care especially of relations between one color and the complement of its adjacent color - in case of the tetrade (90° distance), good feeling and very sensitive approach are necessary.
Analogic colors
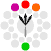 This scheme is made by base color and its adjacent colors - two colors identically on both sides. It always looks very elegantly and clear, the result has less tension and it's uniformly warm, or cold. If a color on the warm-cold border is chosen, the color with opposite "temperature" may be used for accenting the other two colors.
This scheme is made by base color and its adjacent colors - two colors identically on both sides. It always looks very elegantly and clear, the result has less tension and it's uniformly warm, or cold. If a color on the warm-cold border is chosen, the color with opposite "temperature" may be used for accenting the other two colors.
Additional input field sets the distance of adjacent colors - values between 15-30° are optimal. You can also add the contrast color, the scheme is then supplemented with the complement of the base color. It must be treated only as a complement - it adds tension to the palette, and it's too aggressive when overused. However, used in details and as accent of main colors, it can be very effective and elegant.
Contradictory colors
There is no scheme named "contradictory" here - on the contrary, it's a color scheme, which can't fit into any rule described above. This scheme may not be useless - there may be situations, when we have to create shocking, really gaudy, jazzy work. Even in this case this tool may be usefull - if your scheme differs from all described models, you've got it: nervous, loud, aggressive set of colors. Of course, it cannot be suitable for applications requiring not so intensive emotions.
Color palette
The color palette is displayed bellow the color sample. First column contains main colors (according to the chosen scheme). The other columns contain their monochromatic variations (the same in one column). Hex-codes in the table are links; clicking on any of them, you'll set new base color.
Checkbox bellow the color table serves to reduce the palette to "WebColors" (216 safe colors for WWW pages). Nevertheless, this conversion changes shades of colors, and a well-tuned color scheme may be deformed. Therefore, you'd better prefer colors, which differs from their WebColors-equivalents as less as possible.
To keep the impression of the color scheme, monochromatic variations shouldn't be overused - only black and white are often recommended. If you really need other variations, choose just several variants of the base color; possibly one or two variants of other (contrast) colors as well. Another possibility is to use the same variation of all main colors (eg. the same theme in lighter, paler, or darker shades). In general, one application (one WWW page, one web site) shouldn't use - besides black and white - more than six colors (including all variants). This tool hopefully can help you harmonize them.
Licensing
This product is distributed under the BY-NC-SA licence. License for commercial use is not possible.
Color schemes selector
Copyright (c) 2002 pixy
 Monochormatic scheme is based on only one color tint, and uses only variations made by changing its saturation and brightness. Black and white colors are always added. The result is comfortable for eyes, even when using aggressive color. However, it's harder to find accents and highlights.
Monochormatic scheme is based on only one color tint, and uses only variations made by changing its saturation and brightness. Black and white colors are always added. The result is comfortable for eyes, even when using aggressive color. However, it's harder to find accents and highlights. Base color is supplemented with its complement (color on the opposite side of the wheel). One warm and one cold color is always created - we have to consider, which one will be dominant, and if the result should look warm, or cold. Suitable monochromatic variations of this two colors may be added to the scheme.
Base color is supplemented with its complement (color on the opposite side of the wheel). One warm and one cold color is always created - we have to consider, which one will be dominant, and if the result should look warm, or cold. Suitable monochromatic variations of this two colors may be added to the scheme. Base color is supplemented with two colors, placed identically on both sides of its complement. Unlike the "sharp" contrast, this scheme is often more comfortable for the eyes, it's softer, and has more space for balancing warm and cold colors.
Base color is supplemented with two colors, placed identically on both sides of its complement. Unlike the "sharp" contrast, this scheme is often more comfortable for the eyes, it's softer, and has more space for balancing warm and cold colors. This scheme is made by a pair of colors and their complements. It's based on the tetrade - the foursome of colors evenly distributed on the fourths of the color wheel (by 90 degreees). The tetrade is very aggressive color scheme, requiring very good planning and very sensitive approach to relations of these colors.
This scheme is made by a pair of colors and their complements. It's based on the tetrade - the foursome of colors evenly distributed on the fourths of the color wheel (by 90 degreees). The tetrade is very aggressive color scheme, requiring very good planning and very sensitive approach to relations of these colors. This scheme is made by base color and its adjacent colors - two colors identically on both sides. It always looks very elegantly and clear, the result has less tension and it's uniformly warm, or cold. If a color on the warm-cold border is chosen, the color with opposite "temperature" may be used for accenting the other two colors.
This scheme is made by base color and its adjacent colors - two colors identically on both sides. It always looks very elegantly and clear, the result has less tension and it's uniformly warm, or cold. If a color on the warm-cold border is chosen, the color with opposite "temperature" may be used for accenting the other two colors.